domingo, 19 de octubre de 2014
viernes, 17 de octubre de 2014
CELL THEORY
1. All
living things are made up of cells.
2. The cell
is the basic unit of living things.
3. Living
cells come from other living cells.
The history
of this theory started when Robert Hooke, an English scientist, discovered the
cell by looking at a cork through a microscope in 1665. After Hooke, in 1676 Anton
Van Leeuwenhoek find out something he called “animacules”, that are living
cells. Later, he discovered bacteria.
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
discovered that plants (Schleiden) and animals (Schwann) were made up of cells,
and with these discoveries, the first postulate was developed: All living
animals are made up of cells. Later, they also said that cells are the basic
unit of structure of every living thing. After those discoveries, Rudolph
Virchow, discovered that all living things come from other living things;
meaning that living cells come from other living cells (third postulate)
The development
of the cell theory is a good example of scientific inquiry because throughout
its history, all de discoveries were found out by scientific methods and
scientific tools: the microscope.
CELL CYCLE
Is a
process that includes three phases: Growth (interphase), Mitosis (nuclear
division) and Cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division). Growth is when de cell grows
preparing for the nuclear division, and G1, S and G2 happened (DNA
duplication). In mitosis, duplicated chromosomes are split equally, and the
cell prepares for the cytokinesis. In the cytoplasmic division, the cell
finishes splitting and forms two identical cells.
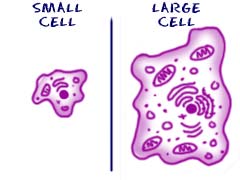
CELL GROWTH
All cells
in a normal status are equal in size. This is because every time, something
wants to enter the cell, it needs to go form de cell wall to the organelles. If
the cell grew more, the distance between de surface area of the cell or the
perimeter and the organelle will be longer and this will make things slower for
every process.
miércoles, 15 de octubre de 2014
MEIOSIS vs. MITOSIS
| Definition | MEIOSIS A type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half | MITOSIS A process of asexual reproduction in which the cell divides in two producing a replica. |
| Function | Make cells genetically diferent by sexual reproduction. | Cellular reproduction. |
| Type of Reproduction | Sexual | Asexual |
| Occurs in | Humans, animals, plants, fungi. | All organisms. |
| Genetically | Different | Identical |
| Creates | Sex cells only (female egg male sperm) | Makes everything other than sex cells. |
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)